Unlike a road hazard that can often be temporarily mitigated via a detour. Rail often has limited choices around alternate routes. Typically, only being able to switch to a parallel track or wait until the obstruction or incident is clear. Depending on the element of rail infrastructure, its physical structure and the dynamics of that location, different hazards will be more prevalent. Requiring a slight variation in detection focus and algorithm.
Rail Infrastructure Applications
Rail Infrastructure Applications
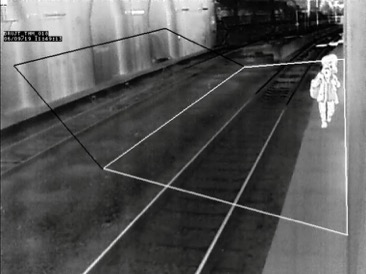
Platforms
Railway platforms that have open air access to the rail line; beyond the edge of the platform, present a fall hazard should a member of the public not watch where they are walking. Whether intentional or not, a fallen person off a railway platform is at serious risk of further injury or death. Should an approaching train not be aware or their presence or be unable to stop in time to prevent a collision. At the fringes of the platform detection of trespass is also important, as it provides an easy access point onto the track system.
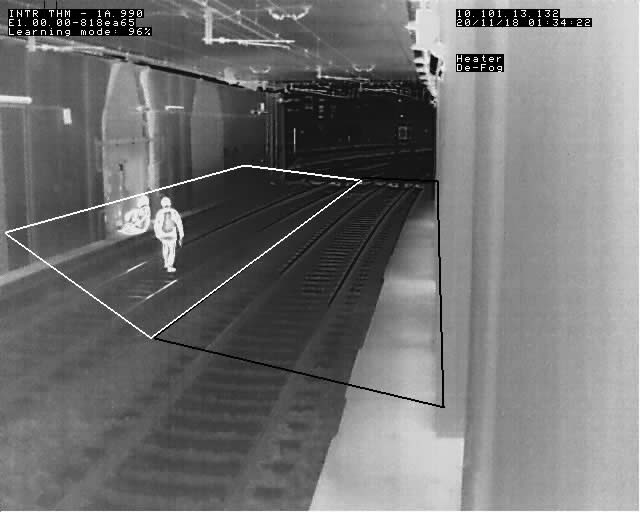

Tunnels
Trespass and vandalism in tunnels is often hard to monitor due to lack of light and concealment from public view. With minimal entry and exit points, a tunnel intruder is at an increased level of danger, as the both the approaching train and intruder most likely will not become aware of the danger until it is too late. At the same time a train driver in a tunnel for the most part is relying on and trusting the track signals to indicate safe and permitted passage. Hence, early detection of a tunnel obstruction is important, so the message can be relayed down the line to approaching trains.

Tracks
Obstruction of tracks can come in many forms. Fallen freight, trees, livestock and humans all present a potential to cause damage and interrupt rail services. Unlike a car driver that can bring a vehicle to a sudden stop, a train will often be unable to stop, carrying the momentum of its multiple carriages well past the impact point. Early detection however, can aid in providing enough time to slow or even stop train before impact. Additionally, awareness of intruders onto the rail line can also aid in alerting Police to facilitate assistance and removal, should the intruder have dire intentions for themselves or others.

Crossings
Level crossings are a high risk area and are typically adorned with flashing lights, boom gates and a loud bell or siren. Although these provide a visual, physical and audible deterrent to entering the crossing, unfortunately on occasion a vehicle; either through error or misjudgement, ends up in the most precarious position. On the railway line, in the path of an oncoming train. As previously mentioned, a train has a limited ability to stop. However, early detection of an obstruction on the level crossing may be able to be communicated to rail staff and also expedite assistance to move the vehicle out of danger.
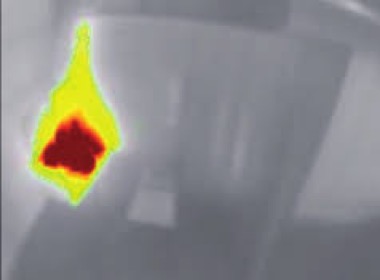
Carriages
Whilst the majority of hazards that will cause disruption and delays are external to the rolling stock of rail. Awareness of fire and monitoring of behaviour within carriages is also important to prevent vandalism and protect public safety. Early detection in the initial stages of ignition can also prevent significant damage to property and harm to the public.

Light Rail
The mixed traffic environment that is inherent to light rail presents an increased risk regarding interaction with vulnerable road users. Although light rail travels at considerably slower speeds that metro rail, exposure is much greater and is continually fluctuating. Along with the fact that during the implementation stage, the public has a low awareness of the existence or history of interaction with light rail. Lacking the development of learned behaviour and automatic responses to the danger presented.

Although with time systems will bed in and awareness and familiarity will rise. Having tracks that are placed on multiuse road surfaces and that transit through public areas, will always present a collision risk to vulnerable road users. This highlights the importance of vigilance for light rail drivers to avoid impacts. However, humans are all susceptible to human error. Whether that be through distraction, fatigue or anything else. This is where thermal imaging automatic detection may provide an additional set of eyes at key points to alert the driver of a hazard or automatically alert the vulnerable road user within the detection zone of their proximity to danger.
